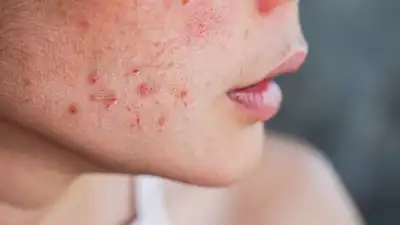
Fungal acne is a common skin condition caused by an overgrowth of yeast called Malassezia in the hair follicles. Unlike regular acne, fungal acne often appears as small, itchy, uniform bumps and tends to show up on areas like the chest, back, shoulders, and face. Warm, humid environments, excessive sweating, and tight clothing can trigger or worsen fungal acne. It’s often confused with regular acne, but it requires a different treatment approach using antifungal products and proper skincare. Recognising the symptoms, causes, and effective prevention strategies is essential for managing and treating fungal acne successfully and keeping your skin healthy.
What is fungal acne and its symptoms
Fungal acne is a skin condition that occurs when the yeast Malassezia grows excessively in the hair follicles. This yeast is naturally found on the skin, but certain conditions can lead to its overgrowth. Fungal acne can appear on various parts of the body, including the face, chest, back, and arms.Fungal acne can be identified by its distinct symptoms, which include:
- Small, uniform bumps: Fungal acne typically appears as small, itchy bumps that are similar in size and shape.
- Itchiness: Fungal acne is often accompanied by intense itching, which can be a distinguishing feature from regular acne.
- Redness and inflammation: The affected area may become red and inflamed.
- Clusters of bumps: Fungal acne can appear in clusters, especially on the chest, back, and shoulders.
Causes of fungal acne
Several factors can contribute to the development of fungal acne, including:
- Excessive sweating: Trapped sweat can create a humid environment that fosters yeast growth.
- Warm and humid environments: Fungal acne thrives in hot and humid climates.
- Occlusive clothing and fabrics: Tight-fitting clothing can trap sweat and heat, promoting fungal growth.
- Skin barrier disruption: Over-exfoliation, harsh soaps, and certain medical conditions can weaken the skin’s protective layer.
- Imbalances in
skin microbiome : Antibiotic use can disrupt the balance of bacteria and yeast on the skin. - Skincare and haircare products: Certain products can contribute to fungal acne, especially those containing oils or heavy ingredients.
Are fungal acne and regular acne similar: Understanding the difference
Fungal acne and regular acne can appear similar, but they have distinct causes and characteristics. Fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast in damaged or blocked hair follicles, while regular acne is caused by blocked hair follicles with dead skin, oil, and bacteria. Fungal acne tends to be itchy, appears as uniform pimples that cluster together, and often occurs on the upper back, chest, and shoulders. In contrast, regular acne can manifest as various types of acne sores and is more common on the face. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment options for fungal acne
Treatment for fungal acne typically involves antifungal medications, which can be topical or oral, and lifestyle changes. Some effective treatment options include:Lifestyle changes: Keeping the affected area clean and dry, wearing breathable clothing, and avoiding heavy skincare products can help manage fungal acne.
Prevention and management of fungal acne
To prevent fungal acne from recurring, it’s essential to maintain good hygiene and make lifestyle adjustments, such as:
- Showering regularly: Remove sweat and bacteria from the skin by showering immediately after exercise or sweating.
- Wearing breathable fabrics: Choose loose-fitting clothing made from natural fabrics like cotton.
- Using antifungal products: Incorporate antifungal cleansers or spot treatments into your skincare routine.
- Avoiding oil-rich products: Opt for oil-free or non-comedogenic products that won’t clog pores or feed the yeast.
Also read | Why you should never pop a pimple: Know its risks and tips to heal