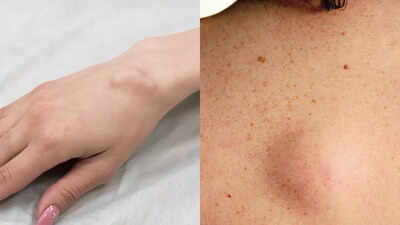
Noticing a lump in your body can be frightening, but not every lump signals danger. Many people mistake cysts for tumours or vice versa, yet understanding the difference is vital for your health. Lumps can appear anywhere, from the skin and soft tissues to organs and bones, but they aren’t all created equal. Cysts are usually fluid-filled and often harmless, while tumours can be solid and may be benign or malignant. Knowing their key differences in appearance, texture, and growth can help you identify warning signs early and seek timely medical attention.
Understanding what a
CystA cyst is a sac-like structure filled with fluid, air, or other material. Cysts can develop in many areas of the body and are generally benign, meaning they are not cancerous. They may feel soft or tender and can often be seen moving around under the skin. Most cysts do not cause symptoms and may not require treatment unless they become painful, infected, or cosmetically concerning.Common examples of cysts include breast cysts, ovarian cysts, sebaceous cysts, and ganglion cysts. While cysts are usually harmless, rare cases can occur where malignant cells are present inside a cyst, known as cystic neoplasms.
TumourA tumour is an abnormal growth of tissue caused by uncontrolled cell division. Tumours can be benign or malignant. Benign tumours remain in one location, grow slowly, and typically do not cause serious issues unless they press on surrounding tissues. Malignant tumours are cancerous, capable of invading nearby tissue and spreading to other parts of the body.Tumours can develop anywhere in the body and may feel firm or hard to the touch. Unlike cysts, tumours are usually solid. Malignant tumours may remain painless in the early stages but can lead to symptoms depending on their size and location.
Key differences between cysts and tumours
While cysts and tumours may look similar, some characteristics help differentiate them. The following table summarises the main differences:
Causes of cysts and tumours
The exact cause of cysts and tumours differs.Cysts often form when glands or ducts become blocked, leading to fluid accumulation. They can also result from tissue injury, infections, or chronic inflammation. Hormonal changes and genetic predispositions further contribute to cyst formation. For instance, a study published in ScienceDirect highlights that certain genetic mutations can lead to the development of cysts, particularly in conditions like polycystic kidney diseaseTumours, on the other hand, arise from abnormal cell growth due to genetic mutations. These mutations can be triggered by carcinogens, radiation, or inherited genetic factors. Tumours can be benign, growing slowly without spreading, or malignant, exhibiting uncontrolled growth and the potential to metastasise. A study published in Nature indicates that tumour development often involves a multistep process, where initial mutations confer a growth advantage to cells, leading to tumourigenesis
How are cysts and tumours diagnosed
Diagnosis begins with a physical examination, but visual inspection alone often cannot determine the difference. Doctors rely on:
- Ultrasound – Identifies whether a lump is fluid-filled (cyst) or solid (tumour).
- CT scans or MRI – Detailed imaging for deeper or internal growths.
- Mammograms – Used for breast lumps.
- Biopsy – The gold standard for distinguishing benign from malignant tissue.
- Fine needle aspiration – Fluid is removed from cysts for analysis.
Even if a lump appears benign, persistent, growing, or irregular lumps may require further evaluation.
Treatment options
For cystsObservation – Most cysts are harmless and may not need treatment.Aspiration or drainage – Fluid can be removed to relieve discomfort.Surgical removal – Necessary if the cyst recurs or becomes problematic.For tumoursBenign tumours – Usually monitored; removal only if they interfere with function or cause discomfort.Malignant tumours- Often require surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these treatments, depending on the type, size, and location.
When to see a doctor
Seek medical attention if a lump:
- Grows quickly or changes shape
- Bleeds, oozes, or changes colour
- Feels hard or fixed
- Becomes painful, red, or swollen
- It is associated with other symptoms like difficulty breathing or joint movement
Early evaluation is crucial for peace of mind and effective treatment, particularly if a tumour is malignant.Cysts and tumours are both types of lumps that can appear throughout the body. While cysts are usually benign, fluid-filled sacs, tumours can be either benign or cancerous, with the potential to grow, invade surrounding tissue, and spread. Physical characteristics can provide clues, but imaging and biopsies are often necessary to confirm the nature of a lump. Any persistent or concerning lump should be evaluated promptly to ensure proper care and peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. When should I see a doctor?Seek medical attention if a lump bleeds, changes colour, grows quickly, itches, ruptures, or looks red/swollen.Q. Do tumours hurt when pressed?Some benign tumours can be tender, but malignant tumours are often painless initially.Q. Are cysts hard or soft?Cysts can be either soft or firm, depending on the type. Soft cysts are usually benign, though exceptions exist.Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet, medication, or lifestyle.Also read | Bowel cancer prevention tips: 9 lifestyle habits that lower your risk of colon cancer